From the start, MediaWiki was developed specifically to be Wikipedia's software. Developers have worked to facilitate reuse by third-party users, but Wikipedia's influence and bias have shaped MediaWiki's architecture throughout its history.
Wikipedia is one of the top ten websites in the world, currently getting about 400 million unique visitors a month. It gets over 100,000 hits per second. Wikipedia isn't commercially supported by ads; it is entirely supported by a non-profit organization, the Wikimedia Foundation, which relies on donations as its primary funding model. This means that MediaWiki must not only run a top-ten website, but also do so on a shoestring budget. To meet these demands, MediaWiki has a heavy bias towards performance, caching and optimization. Expensive features that can't be enabled on Wikipedia are either reverted or disabled through a configuration variable; there is an endless balance between performance and features.
The influence of Wikipedia on MediaWiki's architecture isn't limited to performance. Unlike generic content management systems (CMSes), MediaWiki was originally written for a very specific purpose: supporting a community that creates and curates freely reusable knowledge on an open platform. This means, for example, that MediaWiki doesn't include regular features found in corporate CMSes, like a publication workflow or access control lists, but does offer a variety of tools to handle spam and vandalism.
So, from the start, the needs and actions of a constantly evolving community of Wikipedia participants have affected MediaWiki's development, and vice versa. The architecture of MediaWiki has been driven many times by initiatives started or requested by the community, such as the creation of Wikimedia Commons, or the Flagged Revisions feature. Developers made major architectural changes because the way that MediaWiki was used by Wikipedians made it necessary.
MediaWiki has also gained a solid external user base by being open source software from the beginning. Third-party reusers know that, as long as such a high-profile website as Wikipedia uses MediaWiki, the software will be maintained and improved. MediaWiki used to be really focused on Wikimedia sites, but efforts have been made to make it more generic and better accommodate the needs of these third-party users. For example, MediaWiki now ships with an excellent web-based installer, making the installation process much less painful than when everything had to be done via the command line and the software contained hardcoded paths for Wikipedia.
Still, MediaWiki is and remains Wikipedia's software, and this shows throughout its history and architecture.
This chapter is organized as follows:
Wikipedia was launched in January 2001. At the time, it was mostly an experiment to try to boost the production of content for Nupedia, a free-content, but peer-reviewed, encyclopedia created by Jimmy Wales. Because it was an experiment, Wikipedia was originally powered by UseModWiki, an existing GPL wiki engine written in Perl, using CamelCase and storing all pages in individual text files with no history of changes made.
It soon appeared that CamelCase wasn't really appropriate for naming encyclopedia articles. In late January 2001, UseModWiki developer and Wikipedia participant Clifford Adams added a new feature to UseModWiki: free links; i.e., the ability to link to pages with a special syntax (double square brackets), instead of automatic CamelCase linking. A few weeks later, Wikipedia upgraded to the new version of UseModWiki supporting free links, and enabled them.
While this initial phase isn't about MediaWiki per se, it provides some context and shows that, even before MediaWiki was created, Wikipedia started to shape the features of the software that powered it. UseModWiki also influenced some of MediaWiki's features; for example, its markup language. The Nostalgia Wikipedia contains a complete copy of the Wikipedia database from December 2001, when Wikipedia still used UseModWiki.
In 2001, Wikipedia was not yet a top ten website; it was an obscure project sitting in a dark corner of the Interwebs, unknown to most search engines, and hosted on a single server. Still, performance was already an issue, notably because UseModWiki stored its content in a flat file database. At the time, Wikipedians were worried about being inundated with traffic following articles in the New York Times, Slashdot and Wired.
So in summer 2001, Wikipedia participant Magnus Manske (then a university student) started to work on a dedicated Wikipedia wiki engine in his free time. He aimed to improve Wikipedia's performance using a database-driven app, and to develop Wikipedia-specific features that couldn't be provided by a "generic" wiki engine. Written in PHP and MySQL-backed, the new engine was simply called the "PHP script", "PHP wiki", "Wikipedia software" or "phase II".
The PHP script was made available in August 2001, shared on SourceForge in September, and tested until late 2001. As Wikipedia suffered from recurring performance issues because of increasing traffic, the English language Wikipedia eventually switched from UseModWiki to the PHP script in January 2002. Other language versions also created in 2001 were slowly upgraded as well, although some of them would remain powered by UseModWiki until 2004.
As PHP software using a MySQL database, the PHP script was the first iteration of what would later become MediaWiki. It introduced many critical features still in use today, like namespaces to organize content (including talk pages), skins, and special pages (including maintenance reports, a contributions list and a user watchlist).
Despite the improvements from the PHP script and database backend, the combination of increasing traffic, expensive features and limited hardware continued to cause performance issues on Wikipedia. In 2002, Lee Daniel Crocker rewrote the code again, calling the new software "Phase III" (http://article.gmane.org/gmane.science.linguistics.wikipedia.technical/2794). Because the site was experiencing frequent difficulties, Lee thought there "wasn't much time to sit down and properly architect and develop a solution", so he "just reorganized the existing architecture for better performance and hacked all the code". Profiling features were added to track down slow functions.
The Phase III software kept the same basic interface, and was designed to look and behave as much like the Phase II software as possible. A few new features were also added, like a new file upload system, side-by-side diffs of content changes, and interwiki links.
Other features were added over 2002, like new maintenance special pages, and the "edit on double click" option. Performance issues quickly reappeared, though. For example, in November 2002, administrators had to temporarily disable the "view count" and "site" statistics which were causing two database writes on every page view. They would also occasionally switch the site to read-only mode to maintain the service for readers, and disable expensive maintenance pages during high-access times because of table locking problems.
In early 2003, developers discussed whether they should properly re-engineer and re-architect the software from scratch, before the fire-fighting became unmanageable, or continue to tweak and improve the existing code base. They chose the latter solution, mostly because most developers were sufficiently happy with the code base, and confident enough that further iterative improvements would be enough to keep up with the growth of the site.
In June 2003, administrators added a second server, the first database server separate from the web server. (The new machine was also the web server for non-English Wikipedia sites.) Load-balancing between the two servers would be set up later that year. Admins also enabled a new page-caching system that used the file system to cache rendered, ready-to-output pages for anonymous users.
June 2003 is also when Jimmy Wales created the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation to support Wikipedia and manage its infrastructure and day-to-day operations. The "Wikipedia software" was officially named "MediaWiki" in July, as wordplay on the Wikimedia Foundation's name. What was thought at the time to be a clever pun would confuse generations of users and developers.
New features were added in July, like the automatically generated table of contents and the ability to edit page sections, both still in use today. The first release under the name "MediaWiki" happened in August 2003, concluding the long genesis of an application whose overall structure would remain fairly stable from there on.
PHP was chosen as the framework for Wikipedia's "Phase II" software in 2001; MediaWiki has grown organically since then, and is still evolving. Most MediaWiki developers are volunteers contributing in their free time, and there were very few of them in the early years. Some software design decisions or omissions may seem wrong in retrospect, but it's hard to criticize the founders for not implementing some abstraction which is now found to be critical, when the initial code base was so small, and the time taken to develop it so short.
For example, MediaWiki uses unprefixed class names, which can cause
conflicts when PHP core and PECL (PHP Extension Community Library)
developers add new classes: MediaWiki Namespace class had to be
renamed to MWNamespace to be compatible with PHP
5.3. Consistently using a prefix for all classes (e.g., "MW")
would have made it easier to embed MediaWiki inside another
application or library.
Relying on PHP was probably not the best choice for performance, since it has not benefitted from improvements that some other dynamic languages have seen. Using Java would have been much better for performance, and simplified execution scaling for back-end maintenance tasks. On the other hand, PHP is very popular, which facilitates recruiting new developers.
Even if MediaWiki still contains "ugly" legacy code, major
improvements have been made over the years, and new architectural
elements have been introduced to MediaWiki throughout its
history. They include the Parser, SpecialPage, and
Database classes, the Image class and the
FileRepo class hierarchy, ResourceLoader, and the Action
hierarchy. MediaWiki started without any of these things, but all of
them support features that have been around since the beginning. Many
developers are interested primarily in feature development and
architecture is often left behind, only to catch up later as the cost
of working within an inadequate architecture becomes apparent.
Because MediaWiki is the platform for high-profile sites such as
Wikipedia, core developers and code reviewers have enforced strict
security rules. (See the
detailed guide.) To make it easier to write secure code, MediaWiki
gives developers wrappers around HTML output and database queries to
handle escaping. To sanitize user input, a develop uses the
WebRequest class, which analyzes data passed in the URL or via
a POSTed form. It removes "magic quotes" and slashes, strips illegal input
characters and normalizes Unicode sequences. Cross-site request
forgery (CSRF) is avoided by using tokens, and cross-site scripting
(XSS) by validating inputs and escaping outputs, usually with PHP's
htmlspecialchars() function. MediaWiki also provides (and uses)
an XHTML sanitizer with the Sanitizer class, and database
functions that prevent SQL injection.
MediaWiki offers hundreds of configuration settings, stored in global
PHP variables. Their default value is set in
DefaultSettings.php, and the system administrator can override
them by editing LocalSettings.php.
MediaWiki used to over-depend on global variables, including for
configuration and context processing. Globals cause serious security
implications with PHP's register_globals function (which
MediaWiki hasn't needed since version 1.2). This system also limits
potential abstractions for configuration, and makes it more difficult
to optimize the start-up process. Moreover, the configuration
namespace is shared with variables used for registration and object
context, leading to potential conflicts. From a user perspective,
global configuration variables have also made MediaWiki seem difficult
to configure and maintain. MediaWiki development has been a story of
slowly moving context out of global variables and into
objects. Storing processing context in object member variables allows
those objects to be reused in a much more flexible way.
MediaWiki has been using a relational database backend since the Phase II software. The default (and best-supported) database management system (DBMS) for MediaWiki is MySQL, which is the one that all Wikimedia sites use, but other DBMSes (such as PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQLite) have community-supported implementations. A sysadmin can choose a DBMS while installing MediaWiki, and MediaWiki provides both a database abstraction and a query abstraction layer that simplify database access for developers.

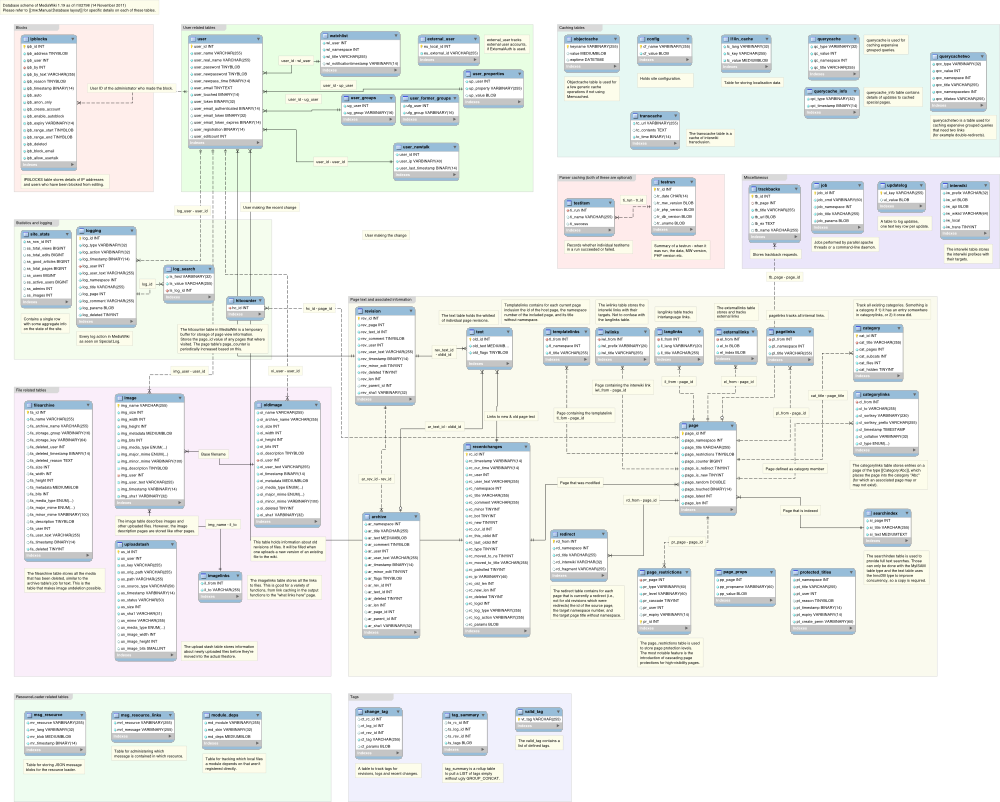
The current layout contains dozens of tables. Many are about the
wiki's content (e.g., page, revision, category,
and recentchanges). Other tables include data about users
(user,
user_groups), media files (image,
filearchive), caching (objectcache, l10n_cache,
querycache) and internal tools (job for the job queue),
among others, as shown in
Figure 12.2.
(Complete documentation of the database layout in
MediaWiki is available.)
Indices
and summary tables are used extensively in MediaWiki, since SQL
queries that scan huge numbers of rows can be very expensive,
particularly on Wikimedia sites. Unindexed queries are usually
discouraged.
The database went through dozens of schema changes over the years, the most notable being the decoupling of text storage and revision tracking in MediaWiki 1.5.

In the 1.4 model, the content was stored in two important tables,
cur (containing the text and metadata of the current revision
of the page) and old (containing previous revisions); deleted
pages were kept in archive. When an edit was made, the
previously current revision was copied to the old table, and
the new edit was saved to cur. When a page was renamed, the
page title had to be updated in the metadata of all the old
revisions, which could be a long operation. When a page was deleted,
its entries in both the cur and old tables had to be
copied to the archive table before being deleted; this meant
moving the text of all revisions, which could be very large and thus
take time.
In the 1.5 model, revision metadata and revision text were split: the
cur and old tables were replaced with page (pages'
metadata), revision (metadata for all revisions, old or
current) and text (text of all revisions, old, current or
deleted). Now, when an edit is made, revision metadata don't need to
be copied around tables: inserting a new entry and updating the
page_latest pointer is enough. Also, the revision metadata
don't include the page title anymore, only its ID: this removes the
need for renaming all revisions when a page is renamed
The revision table stores metadata for each revision, but not
their text; instead, they contain a text ID pointing to the
text table, which contains the actual text. When a page is
deleted, the text of all revisions of the page stays there and doesn't
need to be moved to another table. The text table is composed
of a mapping of IDs to text blobs; a flags field indicates if the text
blob is gzipped (for space savings) or if the text blob is only a
pointer to external text storage. Wikimedia sites use a MySQL-backed
external storage cluster with blobs of a few dozen revisions. The
first revision of the blob is stored in full, and following revisions
to the same page are stored as diffs relative to the previous
revision; the blobs are then gzipped. Because the revisions are
grouped per page, they tend to be similar, so the diffs are relatively
small and gzip works well. The compression ratio achieved on Wikimedia
sites nears 98%.
On the hardware side, MediaWiki has built-in support for load balancing, added as early as 2004 in MediaWiki 1.2 (when Wikipedia got its second server—a big deal at the time). The load balancer (MediaWiki's PHP code that decides which server to connect to) is now a critical part of Wikimedia's infrastructure, which explains its influence on some algorithm decisions in the code. The system administrator can specify, in MediaWiki's configuration, that there is one master database server and any number of slave database servers; a weight can be assigned to each server. The load balancer will send all writes to the master, and will balance reads according to the weights. It also keeps track of the replication lag of each slave. If a slave's replication lag exceeds 30 seconds, it will not receive any read queries to allow it to catch up; if all slaves are lagged more than 30 seconds, MediaWiki will automatically put itself in read-only mode.
MediaWiki's "chronology protector" ensures that replication lag never causes a user to see a page that claims an action they've just performed hasn't happened yet: for instance, if a user renames a page, another user may still see the old name, but the one who renamed will always see the new name, because he's the one who renamed it. This is done by storing the master's position in the user's session if a request they made resulted in a write query. The next time the user makes a read request, the load balancer reads this position from the session, and tries to select a slave that has caught up to that replication position to serve the request. If none is available, it will wait until one is. It may appear to other users as though the action hasn't happened yet, but the chronology remains consistent for each user.
index.php is the main entry point for MediaWiki, and handles
most requests processed by the application servers (i.e., requests that
were not served by the caching infrastructure; see below). The
code executed from index.php performs security checks, loads
default configuration settings from
includes/DefaultSettings.php, guesses configuration with
includes/Setup.php and then applies site settings contained in
LocalSettings.php. Next it instantiates a MediaWiki
object ($mediawiki), and creates a Title object
($wgTitle) depending on the title and action parameters from
the request.
index.php can take a variety of action parameters in the URL
request; the default action is view, which shows the regular
view of an article's content. For example, the request
https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Apple&action=view
displays the content of the article "Apple" on the English
Wikipedia. (View requests are usually prettified with URL
rewriting, in this example to
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple.) Other frequent actions
include edit (to open an article for editing), submit
(to preview or save an article), history (to show an article's
history) and watch (to add an article to the user's
watchlist). Administrative actions include delete (to delete an
article) and protect (to prevent edits to an article).
MediaWiki::performRequest() is then called to handle most of
the URL request. It checks for bad titles, read restrictions, local
interwiki redirects, and redirect loops, and determines whether the
request is for a normal or a special page.
Normal page requests are handed over to
MediaWiki::initializeArticle(), to create an Article
object for the page ($wgArticle), and then to
MediaWiki::performAction(), which handles "standard"
actions. Once the action has been completed,
MediaWiki::finalCleanup() finalizes the request by committing
database transactions, outputting the HTML and launching deferred
updates through the job queue. MediaWiki::restInPeace() commits
the deferred updates and closes the task gracefully.
If the page requested is a Special page (i.e., not a regular wiki
content page, but a special software-related page such as
Statistics), SpecialPageFactory::executePath is called
instead of initializeArticle(); the corresponding PHP script is
then called. Special pages can do all sorts of magical things, and
each has a specific purpose, usually independent of any one article or
its content. Special pages include various kinds of reports (recent
changes, logs, uncategorized pages) and wiki administration tools
(user blocks, user rights changes), among others. Their execution
workflow depends on their function.
Many functions contain profiling code, which makes it possible to
follow the execution workflow for debugging if profiling is
enabled. Profiling is done by calling the wfProfileIn and
wfProfileOut functions to respectively start and stop profiling
a function; both functions take the function's name as a parameter. On
Wikimedia sites, profiling is done for a percentage of all requests,
to preserve performance. MediaWiki sends UDP packets to a central
server that collects them and produces profiling data.
MediaWiki itself is improved for performance because it plays a
central role on Wikimedia sites, but it is also part of a larger
operational ecosystem that has influenced its
architecture. Wikimedia's caching infrastructure (structured in
layers) has imposed limitations in MediaWiki; developers worked around
the issues, not by trying to shape Wikimedia's extensively optimized
caching infrastructure around MediaWiki, but rather by making
MediaWiki more flexible, so it could work within that infrastructure
without compromising on performance and caching needs. For example, by
default MediaWiki displays the user's IP in the top-right corner of
the interface (for left-to-right languages) as a reminder that that's
how they're known to the software when they're not logged in. The
$wgShowIPinHeader configuration variable allows the system
administrator to disable this feature, thus making the page content
independent of the user: all anonymous visitors can then be served the
exact same version of each page.
The first level of caching (used on Wikimedia sites) consists of reverse caching proxies (Squids) that intercept and serve most requests before they make it to the MediaWiki application servers. Squids contain static versions of entire rendered pages, served for simple reads to users who aren't logged in to the site. MediaWiki natively supports Squid and Varnish, and integrates with this caching layer by, for example, notifying them to purge a page from the cache when it has been changed. For logged-in users, and other requests that can't be served by Squids, Squid forwards the requests to the web server (Apache).
The second level of caching happens when MediaWiki renders and assembles the page from multiple objects, many of which can be cached to minimize future calls. Such objects include the page's interface (sidebar, menus, UI text) and the content proper, parsed from wikitext. The in-memory object cache has been available in MediaWiki since the early 1.1 version (2003), and is particularly important to avoid re-parsing long and complex pages.
Login session data can also be stored in memcached, which lets sessions work transparently on multiple front-end web servers in a load-balancing setup (Wikimedia heavily relies on load balancing, using LVS with PyBal).
Since version 1.16, MediaWiki uses a dedicated object cache for localized UI text; this was added after noticing that a large part of the objects cached in memcached consisted of UI messages localized into the user's language. The system is based on fast fetches of individual messages from constant databases (CDB), e.g., files with key-value pairs. CDBs minimize memory overhead and start-up time in the typical case; they're also used for the interwiki cache.
The last caching layer consists of the PHP opcode cache, commonly enabled to speed up PHP applications. Compilation can be a lengthy process; to avoid compiling PHP scripts into opcode every time they're invoked, a PHP accelerator can be used to store the compiled opcode and execute it directly without compilation. MediaWiki will "just work" with many accelerators such as APC, PHP accelerator and eAccelerator.
Because of its Wikimedia bias, MediaWiki is optimized for this complete, multi-layer, distributed caching infrastructure. Nonetheless, it also natively supports alternate setups for smaller sites. For example, it offers an optional simplistic file caching system that stores the output of fully rendered pages, like Squid does. Also, MediaWiki's abstract object caching layer lets it store the cached objects in several places, including the file system, the database, or the opcode cache.
As in many web applications, MediaWiki's interface has become more interactive and responsive over the years, mostly through the use of JavaScript. Usability efforts initiated in 2008, as well as advanced media handling (e.g., online editing of video files), called for dedicated front-end performance improvements.
To optimize the delivery of JavaScript and CSS assets, the ResourceLoader module was developed to optimize delivery of JS and CSS. Started in 2009, it was completed in 2011 and has been a core feature of MediaWiki since version 1.17. ResourceLoader works by loading JS and CSS assets on demand, thus reducing loading and parsing time when features are unused, for example by older browsers. It also minifies the code, groups resources to save requests, and can embed images as data URIs. (For more on ResourceLoader, see the official documentation, and the talk Low Hanging Fruit vs. Micro-optimization: Creative Techniques for Loading Web Pages Faster given by Trevor Parscal and Roan Kattouw at OSCON 2011.)
A central part of effectively contributing and disseminating free knowledge to all is to provide it in as many languages as possible. Wikipedia is available in more than 280 languages, and encyclopedia articles in English represent less than 20% of all articles. Because Wikipedia and its sister sites exist in so many languages, it is important not only to provide the content in the readers' native language, but also to provide a localized interface, and effective input and conversion tools, so that participants can contribute content.
For this reason, localization and internationalization (l10n and i18n) are central components of MediaWiki. The i18n system is pervasive, and impacts many parts of the software; it's also one of the most flexible and feature-rich. (There is an exhaustive guide to internationalization and localization in MediaWiki.) Translator convenience is usually preferred to developer convenience, but this is believed to be an acceptable cost.
MediaWiki is currently localized in more than 350 languages, including non-Latin and right-to-left (RTL) languages, with varying levels of completion. The interface and content can be in different languages, and have mixed directionality.
MediaWiki originally used per-language encoding, which led to a lot of issues; for example, foreign scripts could not be used in page titles. UTF-8 was adopted instead. Support for character sets other than UTF-8 was dropped in 2005, along with the major database schema change in MediaWiki 1.5; content must now be encoded in UTF-8.
Characters not available on the editor's keyboard can be customized and inserted via MediaWiki's Edittools, an interface message that appears below the edit window; its JavaScript version automatically inserts the character clicked into the edit window. The WikiEditor extension for MediaWiki, developed as part of a usability effort, merges special characters with the edit toolbar. Another extension, called Narayam, provides additional input methods and key mapping features for non-ASCII characters.
Interface messages have been stored in PHP arrays of key-values pairs
since the Phase III software was created. Each message is identified
by a unique key, which is assigned different values across
languages. Keys are determined by developers, who are encouraged to
use prefixes for extensions; for example, message keys for the
UploadWizard extension will start with mwe-upwiz-, where
mwe stands for MediaWiki extension.
MediaWiki messages can embed parameters provided by the software, which will often influence the grammar of the message. In order to support virtually any possible language, MediaWiki's localization system has been improved and complexified over time to accommodate languages' specific traits and exceptions, often considered oddities by English speakers.
For example, adjectives are invariable words in English, but languages
like French require adjective agreement with nouns. If the user
specified their gender in their preferences, the {{GENDER:}}
switch can be used in interface messages to appropriately address
them. Other switches include {{PLURAL:}}, for "simple" plurals
and languages like Arabic with dual, trial or paucal numbers, and
{{GRAMMAR:}}, providing grammatical transformation functions
for languages like Finnish whose grammatical cases cause alterations
or inflections.
Localized interface messages for MediaWiki reside in
MessagesXx.php files, where Xx is the ISO-639 code of
the language (e.g. MessagesFr.php for French); default messages
are in English and stored in MessagesEn.php. MediaWiki
extensions use a similar system, or host all localized messages in an
<Extension-name>.i18n.php file. Along
with translations, Message files also include language-dependent
information such as date formats.
Contributing translations used to be done by submitting PHP patches
for the MessagesXx.php files. In December 2003, MediaWiki 1.1
introduced "database messages", a subset of wiki pages in the
MediaWiki namespace containing interface messages. The content of the
wiki page
MediaWiki:<Message-key> is the
message's text, and overrides its value in the PHP file. Localized
versions of the message are at
MediaWiki:<Message-key>/<language-code>;
for example,
MediaWiki:Rollbacklink/de.
This feature has allowed power users to translate (and customize)
interface messages locally on their wiki, but the process doesn't
update i18n files shipping with MediaWiki. In 2006, Niklas Laxström
created a special, heavily hacked MediaWiki website (now hosted at
http://translatewiki.net) where translators can easily localize
interface messages in all languages simply by editing a wiki
page. The MessagesXx.php files are then updated in the
MediaWiki code repository, where they can be automatically fetched by
any wiki, and updated using the LocalisationUpdate extension. On
Wikimedia sites, database messages are now only used for
customization, and not for localization any more. MediaWiki extensions
and some related programs, such as bots, are also localized at
translatewiki.net.
To help translators understand the context and meaning of an interface
message, it is considered a good practice in MediaWiki to provide
documentation for every message. This documentation is stored in a
special Message file, with the qqq language code which doesn't
correspond to a real language. The documentation for each message is
then displayed in the translation interface on
translatewiki.net. Another helpful tool is the qqx language
code; when used with the &uselang parameter to display a
wiki page (e.g.,
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:RecentChanges?uselang=qqx),
MediaWiki will display the message keys instead of their values in the
user interface; this is very useful to identify which message to
translate or change.
Registered users can set their own interface language in their preferences, to override the site's default interface language. MediaWiki also supports fallback languages: if a message isn't available in the chosen language, it will be displayed in the closest possible language, and not necessarily in English. For example, the fallback language for Breton is French.
Users are represented in the code using instances of the User
class, which encapsulates all of the user-specific settings (user id,
name, rights, password, email address, etc.). Client classes use
accessors to access these fields; they do all the work of determining
whether the user is logged in, and whether the requested option can be
satisfied from cookies or whether a database query is needed. Most of
the settings needed for rendering normal pages are set in the cookie
to minimize use of the database.
MediaWiki provides a very granular permissions system, with
a user permission for, basically, every possible action. For example, to perform
the "Rollback" action (i.e., to "quickly rollback the edits of the last
user who edited a particular page"), a user needs the rollback
permission, included by default in MediaWiki's sysop user
group. But it can also be added to other user groups, or have a
dedicated user group only providing this permission (this is the case
on the English Wikipedia, with the Rollbackers
group). Customization of user rights is done by editing the
$wgGroupPermissions array in LocalSettings.php; for
instance, $wgGroupPermissions['user']['movefile'] = true;
allows all registered users to rename files. A user can belong to
several groups, and inherits the highest rights associated with each
of them.
However, MediaWiki's user permissions system was really designed with Wikipedia in mind: a site whose content is accessible to all, and where only certain actions are restricted to some users. MediaWiki lacks a unified, pervasive permissions concept; it doesn't provide traditional CMS features like restricting read or write access by topic or type of content. A few MediaWiki extensions provide such features to some extent.
The concept of namespaces was used in the UseModWiki era of Wikipedia,
where talk pages were at the title "<article
name>/Talk". Namespaces were formally introduced in
Magnus Manske's first "PHP script". They were reimplemented a few
times over the years, but have kept the same function: to separate
different kinds of content. They consist of a prefix separated from
the page title by a colon (e.g. Talk: or File: and
Template:); the main content namespace has no prefix. Wikipedia
users quickly adopted them, and they provided the community with
different spaces to evolve. Namespaces have proven to be an important
feature of MediaWiki, as they create the necessary preconditions for a
wiki's community and set up meta-level discussions, community
processes, portals, user profiles, etc.
The default configuration for MediaWiki's main content namespace is to
be flat (no subpages), because it's how Wikipedia works, but it is
trivial to enable subpages. They are enabled in other namespaces
(e.g., User:, where people can, for instance, work on draft
articles) and display breadcrumbs.
Namespaces separate content by type; within the same namespace, pages can be organized by topic using categories, a pseudo-hierarchical organization scheme introduced in MediaWiki 1.3.
The user-generated content stored by MediaWiki isn't in HTML, but in a markup language specific to MediaWiki, sometimes called "wikitext". It allows users to make formatting changes (e.g. bold, italic using quotes), add links (using square brackets), include templates, insert context-dependent content (like a date or signature), and make an incredible number of other magical things happen. (Detailed documentation is available.)
To display a page, this content needs to be parsed, assembled from all the external or dynamic pieces it calls, and converted to proper HTML. The parser is one of the most essential parts of MediaWiki, which makes it difficult to change or improve. Because hundreds of millions of wiki pages worldwide depend on the parser to continue outputting HTML the way it always has, it has to remain extremely stable.
The markup language wasn't formally specced from the beginning; it started based on UseModWiki's markup, then morphed and evolved as needs demanded. In the absence of a formal specification, the MediaWiki markup language has become a complex and idiosyncratic language, basically only compatible with MediaWiki's parser; it can't be represented as a formal grammar. The current parser's specification is jokingly referred to as "whatever the parser spits out from wikitext, plus a few hundred test cases".
There have been many attempts at alternative parsers, but none has succeeded so far. In 2004 an experimental tokenizer was written by Jens Frank to parse wikitext, and enabled on Wikipedia; it had to be disabled three days later because of the poor performance of PHP array memory allocations. Since then, most of the parsing has been done with a huge pile of regular expressions, and a ton of helper functions. The wiki markup, and all the special cases the parser needs to support, have also become considerably more complex, making future attempts even more difficult.
A notable improvement was Tim Starling's preprocessor rewrite in
MediaWiki 1.12, whose main motivation was to improve the parsing
performance on pages with complex templates. The preprocessor converts
wikitext to an XML DOM tree representing parts of the document
(template invocations, parser functions, tag hooks, section headings,
and a few other structures), but can skip "dead branches",
such as unfollowed #switch cases and unused defaults
for template arguments, in template expansion. The parser then iterates through the DOM
structure and converts its content to HTML.
Recent work on a visual editor for MediaWiki has made it necessary to improve the parsing process (and make it faster), so work has resumed on the parser and intermediate layers between MediaWiki markup and final HTML (see Future, below).
MediaWiki offers "magic words" that modify the general behavior of the
page or include dynamic content into it. They consist of: behavior
switches like __NOTOC__ (to hide the automatic table of
content) or __NOINDEX__ (to tell search engines not to index
the page); variables like {{CURRENTTIME}} or
{{SITENAME}}; and parser functions, i.e., magic words that can
take parameters, like {{lc:<string>}}
(to output <string> in
lowercase). Constructs like {{GENDER:}}, {{PLURAL:}} and
{{GRAMMAR:}}, used to localize the UI, are parser functions.
The most common way to include content from other pages in a MediaWiki page is to use templates. Templates were really intended to be used to include the same content on different pages, e.g., navigation panels or maintenance banners on Wikipedia articles; having the ability to create partial page layouts and reuse them in thousands of articles with central maintenance made a huge impact on sites like Wikipedia.
However, templates have also been used (and abused) by users for a completely different purpose. MediaWiki 1.3 made it possible for templates to take parameters that change their output; the ability to add a default parameter (introduced in MediaWiki 1.6) enabled the construction of a functional programming language implemented on top of PHP, which was ultimately one of the most costly features in terms of performance.
Tim Starling then developed additional parser functions (the
ParserFunctions extension), as a stopgap measure against insane
constructs created by Wikipedia users with templates. This set of
functions included logical structures like #if and
#switch, and other functions like #expr (to evaluate
mathematical expressions) and #time (for time formatting).
Soon enough, Wikipedia users started to create even more complex templates using the new functions, which considerably degraded the parsing performance on template-heavy pages. The new preprocessor introduced in MediaWiki 1.12 (a major architectural change) was implemented to partly remedy this issue. Recently, MediaWiki developers have discussed the possibility of using an actual scripting language, perhaps Lua, to improve performance.
Users upload files through the Special:Upload page;
administrators can configure the allowed file types through an
extension whitelist. Once uploaded, files are stored in a folder on
the file system, and thumbnails in a dedicated thumb directory.
Because of Wikimedia's educational mission, MediaWiki supports file types that may be uncommon in other web applications or CMSes, like SVG vector images, and multipage PDFs and DjVus. They are rendered as PNG files, and can be thumbnailed and displayed inline, as are more common image files like GIFs, JPGs and PNGs.
When a file is uploaded, it is assigned a File: page containing
information entered by the uploader; this is free text and usually
includes copyright information (author, license) and items describing
or classifying the content of the file (description, location, date,
categories, etc.). While private wikis may not care much about this
information, on media libraries like Wikimedia Commons it are
critical to organise the collection and ensure the legality of sharing
these files. It has been argued that most of these metadata should, in
fact, be stored in a queryable structure like a database table. This
would considerably facilitate search, but also attribution and reuse
by third parties—for example, through the API.
Most Wikimedia sites also allow "local" uploads to each wiki, but the community tries to store freely licensed media files in Wikimedia's free media library, Wikimedia Commons. Any Wikimedia site can display a file hosted on Commons as if it were hosted locally. This custom avoids having to upload a file to every wiki to use it there.
As a consequence, MediaWiki natively supports foreign media
repositories, i.e., the ability to access media files hosted on
another wiki through its API and the ForeignAPIRepo
system. Since version 1.16, any MediaWiki website can easily use files
from Wikimedia Commons through the InstantCommons feature. When
using a foreign repository, thumbnails are stored locally to save
bandwidth. However, it is not (yet) possible to upload to a foreign
media repository from another wiki.
MediaWiki's architecture provides different ways to customize and extend the software. This can be done at different levels of access:
External programs can also communicate with MediaWiki through its machine API, if it's enabled, basically making any feature and data accessible to the user.
MediaWiki can read and apply site-wide or skin-wide JavaScript and CSS
using custom wiki pages; these pages are in the MediaWiki:
namespace, and thus can only be edited by sysops; for example,
JavaScript modifications from MediaWiki:Common.js apply to all
skins, CSS from MediaWiki:Common.css applies to all skins, but
MediaWiki:Vector.css only applies to users with the Vector
skin.
Users can do the same types of changes, which will only apply to their
own interface, by editing subpages of their user page
(e.g. User:<Username>/common.js for
JavaScript on all skins,
User:<Username>/common.css for CSS on
all skins, or User:<Username>/vector.css
for CSS modifications that only apply to the Vector skin).
If the Gadgets extension is installed, sysops can also edit gadgets, i.e., snippets of JavaScript code, providing features that can be turned on and off by users in their preferences. Upcoming developments on gadgets will make it possible to share gadgets across wikis, thus avoiding duplication.
This set of tools has had a huge impact and greatly increased the democratization of MediaWiki's software development. Individual users are empowered to add features for themselves; power users can share them with others, both informally and through globally configurable sysop-controlled systems. This framework is ideal for small, self-contained modifications, and presents a lower barrier to entry than heavier code modifications done through hooks and extensions.
When JavaScript and CSS modifications are not enough, MediaWiki provides a system of hooks that let third-party developers run custom PHP code before, after, or instead of MediaWiki code for particular events. (MediaWiki hooks are referenced at https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Hooks.) MediaWiki extensions use hooks to plug into the code.
Before hooks existed in MediaWiki, adding custom PHP code meant modifying the core code, which was neither easy nor recommended. The first hooks were proposed and added in 2004 by Evan Prodromou; many more have been added over the years when needed. Using hooks, it is even possible to extend MediaWiki's wiki markup with additional capabilities using tag extensions.
The extension system isn't perfect; extension registration is based on code execution at startup, rather than cacheable data, which limits abstraction and optimization and hurts MediaWiki's performance. But overall, the extension architecture is now a fairly flexible infrastructure that has helped make specialized code more modular, keeping the core software from expanding (too) much, and making it easier for third-party users to build custom functionality on top of MediaWiki.
Conversely, it's very difficult to write a new skin for MediaWiki
without reinventing the wheel. In MediaWiki, skins are PHP classes
each extending the parent Skin class; they contain functions
that gather the information needed to generate the HTML. The
long-lived "MonoBook" skin was difficult to customize because it
contained a lot of browser-specific CSS to support old browsers;
editing the template or CSS required many subsequent changes to
reflect the change for all browsers and platforms.
The other main entry point for MediaWiki, besides index.php, is
api.php, used to access its machine-readable web query API
(Application Programming Interface).
Wikipedia users originally created "bots" that worked by screen
scraping the HTML content served by MediaWiki; this method was very
unreliable and broke many times. To improve this situation, developers
introduced a read-only interface (located at query.php),
which then evolved into a full-fledged read and write machine API
providing direct, high-level access to the data contained in the
MediaWiki database. (Exhaustive documentation of the API is available.)
Client programs can use the API to login, get data, and post changes. The API supports thin web-based JavaScript clients and end-user applications. Almost anything that can be done via the web interface can basically be done through the API. Client libraries implementing the MediaWiki API are available in many languages, including Python and .NET.
What started as a summer project done by a single volunteer PHP developer has grown into MediaWiki, a mature, stable wiki engine powering a top-ten website with a ridiculously small operational infrastructure. This has been made possible by constant optimization for performance, iterative architectural changes and a team of awesome developers.
The evolution of web technologies, and the growth of Wikipedia, call for ongoing improvements and new features, some of which require major changes to MediaWiki's architecture. This is, for example, the case for the ongoing visual editor project, which has prompted renewed work on the parser and on the wiki markup language, the DOM and final HTML conversion.
MediaWiki is a tool used for very different purposes. Within Wikimedia projects, for instance, it's used to create and curate an encyclopedia (Wikipedia), to power a huge media library (Wikimedia Commons), to transcribe scanned reference texts (Wikisource), and so on. In other contexts, MediaWiki is used as a corporate CMS, or as a data repository, sometimes combined with a semantic framework. These specialized uses that weren't planned for will probably continue to drive constant adjustments to the software's internal structure. As such, MediaWiki's architecture is very much alive, just like the immense community of users it supports.
This chapter was created collaboratively. Guillaume Paumier wrote most of the content by organizing the input provided by MediaWiki users and core developers. Sumana Harihareswara coordinated the interviews and input-gathering phases. Many thanks to Antoine Musso, Brion Vibber, Chad Horohoe, Tim Starling, Roan Kattouw, Sam Reed, Siebrand Mazeland, Erik Möller, Magnus Manske, Rob Lanphier, Amir Aharoni, Federico Leva, Graham Pearce and others for providing input and/or reviewing the content.